Language Features
Powerful features designed for mathematical computing with a clean, intuitive syntax
Data Types
Support for int and float primitive types, with automatic type conversion for mathematical operations.
float y = 3.14;
// Automatic conversion to float when mixing types
float result = x + y;
Arrays
Dynamic and static arrays with support for both integer and float types. Arrays are passed by reference.
int[size] dynamicArray;
float[] floatArray;
Functions
Support for function declarations, parameters, and recursive functions with proper return types.
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
}
Control Structures
Traditional control flow with if-else statements and while loops for iterative programming.
printf("Minor\n");
} else {
printf("Adult\n");
}
while (i < 10) {
i = i + 1;
}
I/O Operations
C-style input/output with printf and scanf functions for formatted input and output.
scanf("%ld", age);
printf("You are %d years old\n", age);
Mathematical Operations
Full support for arithmetic, logical, and relational operators with proper precedence.
bool condition = x > 0 && y < 100;
float division = x / y;
Compiler Architecture
The Balbismo compiler is built using a modern pipeline that generates LLVM IR code for optimal performance and portability.
1. Lexical Analysis
Flex (lexical analyzer) tokenizes the source code
2. Syntax Analysis
Bison (parser generator) builds the Abstract Syntax Tree
3. Semantic Analysis
Dart-based semantic analyzer with symbol table
4. Code Generation
LLVM IR generation for cross-platform compilation
Compilation Modes
Generate IR
Generates LLVM Intermediate Representation code
Optimize IR
Generates optimized LLVM IR using LLVM's optimization passes
Generate Assembly
Generates target-specific assembly code
Compile Binary
Compiles to native executable binary
Run Directly
Compiles and executes the program immediately
Choose Your Mode
Multiple compilation options for different use cases and performance requirements
Code Examples
Explore the power and simplicity of Balbismo through practical examples
Hello World
printf("Hello, World!\n");
}
Mathematical Operations
int x = 5;
int y = -2;
float z = 30.3;
// Automatic float conversion
printf("%f\n", 10 + y + x - 1.2 + z);
}
Conditional Statements
int age;
printf("Enter your age:\n");
scanf("%ld", age);
if (age < 12) {
printf("child\n");
} else if (age <= 15) {
printf("pre adolescent\n");
} else {
printf("adult\n");
}
}
[waits for user input]
Example outputs:
child (if age < 12)
pre adolescent (if age ≤ 15)
adult (if age > 15)
Arrays and Functions
int total = 0;
int i = 0;
while (i < size) {
total = total + nums[i];
i = i + 1;
}
return total;
}
int main() {
int[3] arr;
arr[0] = 1;
arr[1] = 2;
arr[2] = 3;
printf("Sum: %d\n", sum(arr, 3));
}
6.000000
Recursive Functions
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
}
int main() {
int n = 5;
printf("Factorial of %d is %d\n", n, factorial(n));
}
Array References & Dynamic Sizing
// therefore can be modified inside functions
int fillArray(int[] arr, int number, int size) {
int i = 0;
while (i < size) {
arr[i] = number;
i = i + 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
int arraySize;
printf("Choose the size of the array:\n");
scanf("%ld", arraySize);
int[arraySize] arr;
fillArray(arr, 5, arraySize);
printArray(arr, arraySize);
fillArray(arr, 7, arraySize);
printArray(arr, arraySize);
}
[User input: 3]
5 5 5
Choose a new number to fill array:
[User input: 7]
7 7 7
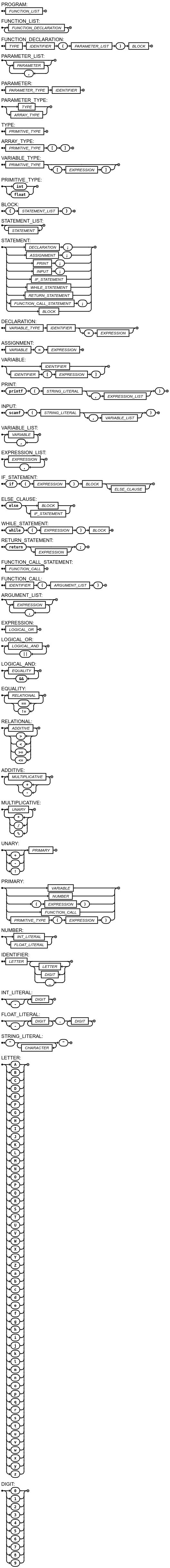
Language Grammar
Balbismo follows a clean, C-like syntax with support for mathematical operations and structured programming.
Identifiers
Variable and function names can contain letters, digits, and underscores, starting with a letter.
Numbers
Support for integer and floating-point literals with optional negative signs.
Strings
String literals enclosed in double quotes for printf and scanf functions.
Arrays
Array types with optional size specification and array access with index expressions.