Balbismo Language Guide
Deep dive into the Balbismo programming language: syntax, semantics, types, arrays, control flow, expressions, casting, I/O, and code generation model.
Types
Balbismo provides two primitive numeric types: int and float. Integers map to LLVM i64; floats map to double.
float b = 1.5;
// explicit cast
int c = int(3.2);
float d = float(7);
Implicit numeric promotion happens in expressions: if an operand is float, the other int is promoted to float for the operation.
🔍 View Generated LLVM IR
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
declare i32 @scanf(i8*, ...)
define i64 @main() {
entry:
%ptr.a.6 = alloca i64
%val5 = add i64 0, 10
store i64 %val5, ptr %ptr.a.6
%ptr.b.10 = alloca double
%val9 = fadd double 0.0, 1.5
store double %val9, ptr %ptr.b.10
%ptr.c.15 = alloca i64
%val13 = fadd double 0.0, 3.2
%conv.14 = fptosi double %val13 to i64
store i64 %val14, ptr %ptr.c.15
%ptr.d.20 = alloca double
%val18 = add i64 0, 7
%conv.19 = sitofp i64 %val18 to double
store double %val19, ptr %ptr.d.20
%val21 = add i64 0, 0
ret i64 %val21
}Arrays
Arrays are homogenous (int or float) and support runtime sizes in declarations. They are stack-allocated (via alloca) and not resizable after creation.
int[size] arr;
arr[0] = 10;
arr[1] = 20;
arr[2] = 30;
The size expression may be computed at runtime. Arrays are passed by reference (pointer semantics). Assigning an entire array is not allowed; assign element-by-element.
🔍 View Generated LLVM IR
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
declare i32 @scanf(i8*, ...)
define i64 @main() {
entry:
%ptr.size.8 = alloca i64
%val5 = add i64 0, 1
%val6 = add i64 0, 2
%binOp.7 = add i64 %val5, %val6
store i64 %binOp.7, ptr %ptr.size.8
%var10 = load i64, ptr %ptr.size.8
%arrayptr.14 = alloca i64, i64 %var10
%ptr.arr.14 = getelementptr i64, i64* %arrayptr.14, i64 0
%val17 = add i64 0, 10
%val15 = add i64 0, 0
%arrayPtr.18 = getelementptr i64, i64* %ptr.arr.14, i64 %val15
store i64 %val17, ptr %arrayPtr.18
%val21 = add i64 0, 20
%val19 = add i64 0, 1
%arrayPtr.22 = getelementptr i64, i64* %ptr.arr.14, i64 %val19
store i64 %val22, ptr %arrayPtr.22
%val25 = add i64 0, 30
%val23 = add i64 0, 2
%arrayPtr.26 = getelementptr i64, i64* %ptr.arr.14, i64 %val23
store i64 %val25, ptr %arrayPtr.26
%val27 = add i64 0, 0
ret i64 %val27
}Functions
Functions have typed parameters and a return type. Recursion is supported. Arrays in parameters behave as references.
int i = 0;
int s = 0;
while (i < n) {
s = s + a[i];
i = i + 1;
}
return s;
}
At codegen, parameters are allocated and stored into stack slots. Arrays keep their pointer.
🔍 View Generated LLVM IR
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
declare i32 @scanf(i8*, ...)
define i64 @sum(i64* %a , i64 %n ) {
entry:
%ptr.n.38 = alloca i64
store i64 %n, ptr %ptr.n.38
%ptr.i.14 = alloca i64
%val13 = add i64 0, 0
store i64 %val13, ptr %ptr.i.14
%ptr.s.18 = alloca i64
%val17 = add i64 0, 0
store i64 %val17, ptr %ptr.s.18
br label %while.34
while.34:
%var19 = load i64, ptr %ptr.i.14
%var20 = load i64, ptr %ptr.n.38
%temp.21 = icmp slt i64 %var19, %var20
%relOp.21 = zext i1 %temp.21 to i64
%conditionCast.34 = icmp ne i64 %relOp.21, 0
br i1 %conditionCast.34, label %block.34, label %end.34
block.34:
%var23 = load i64, ptr %ptr.s.18
%var24 = load i64, ptr %ptr.i.14
%arrayPtr.25 = getelementptr i64, i64* %a, i64 %var24
%var25 = load i64, ptr %arrayPtr.25
%binOp.26 = add i64 %var23, %var25
store i64 %binOp.26, ptr %ptr.s.18
%var29 = load i64, ptr %ptr.i.14
%val30 = add i64 0, 0, 1
%binOp.31 = add i64 %var29, %val30
store i64 %binOp.31, ptr %ptr.i.14
br label %while.34
end.34:
%var35 = load i64, ptr %ptr.s.18
ret i64 %var35
}
define i64 @main() {
entry:
%val43 = add i64 0, 3
%arrayptr.47 = alloca i64, i64 %val43
%ptr.arr.47 = getelementptr i64, i64* %arrayptr.47, i64 0
%val50 = add i64 0, 1
%val48 = add i64 0, 0
%arrayPtr.51 = getelementptr i64, i64* %ptr.arr.47, i64 %val48
store i64 %val50, ptr %arrayPtr.51
%val54 = add i64 0, 2
%val52 = add i64 0, 1
%arrayPtr.55 = getelementptr i64, i64* %ptr.arr.55, i64 %val52
store i64 %val54, ptr %arrayPtr.55
%val58 = add i64 0, 3
%val56 = add i64 0, 2
%arrayPtr.59 = getelementptr i64, i64* %ptr.arr.47, i64 %val56
store i64 %val58, ptr %arrayPtr.59
%ptr.result.67 = alloca i64
%val64 = add i64 0, 3
%call.66 = call i64 @sum(i64* %ptr.arr.47, i64 %val64)
store i64 %call.66, ptr %ptr.result.67
%val68 = add i64 0, 0
ret i64 %val68
}Control Flow
Traditional if / else and while. Conditions evaluate to int values; nonzero is true.
scanf("%ld", age);
if (age < 18) {
printf("Minor\n");
} else {
printf("Adult\n");
}
Conditional branches lower to LLVM br i1 after comparing against zero.
🔍 View Generated LLVM IR
@str.2 = private constant [7 x i8] c"Adult\0A\00"
@str.1 = private constant [7 x i8] c"Minor\0A\00"
@str.0 = private constant [4 x i8] c"%ld\00"
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
declare i32 @scanf(i8*, ...)
define i64 @main() {
entry:
%ptr.age.5 = alloca i64
call i32 (i8*, ...) @scanf(i8* @str.0, i64* %ptr.age.5)
%var9 = load i64, ptr %ptr.age.5
%val10 = add i64 0, 18
%temp.11 = icmp slt i64 %var9, %val10
%relOp.11 = zext i1 %temp.11 to i64
%conditionCast.18 = icmp ne i64 %relOp.11, 0
br i1 %conditionCast.18, label %then.18, label %else.18
then.18:
call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* @str.1)
br label %end.18
else.18:
call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* @str.2)
br label %end.18
end.18:
%val19 = add i64 0, 0
ret i64 %val19
}Expressions & Operators
Arithmetic: + - * / %. Relational: == != < > <= >=. Logical: && || !.
float b = 2.0;
printf("%f\n", a + b); // a promoted to float
Mixed int/float expressions promote to float. Logical and relational results are represented as int (0/1).
🔍 View Generated LLVM IR
@str.0 = private constant [4 x i8] c"%f\0A\00"
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
declare i32 @scanf(i8*, ...)
define i64 @main() {
entry:
%ptr.a.6 = alloca i64
%val5 = add i64 0, 5
store i64 %val5, ptr %ptr.a.6
%ptr.b.10 = alloca double
%val9 = fadd double 0.0, 2.0
store double %val9, ptr %ptr.b.10
%var12 = load i64, ptr %ptr.a.6
%var13 = load double, ptr %ptr.b.10
%conv.14 = sitofp i64 %var12 to double
%binOp.14 = fadd double %conv.14, %var13
call i32 (i8*, ...) @printf(i8* @str.0, double %binOp.14)
%val16 = add i64 0, 0
ret i64 %val16
}Casting
Explicit casts use the form int(expr) or float(expr).
float y = float(x);
float z = 3.14;
int w = int(z);
Casts lower to LLVM sitofp and fptosi as appropriate.
🔍 View Generated LLVM IR
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
declare i32 @scanf(i8*, ...)
define i64 @main() {
entry:
%ptr.x.6 = alloca i64
%val5 = add i64 0, 3
store i64 %val5, ptr %ptr.x.6
%ptr.y.11 = alloca double
%var9 = load i64, ptr %ptr.x.6
%conv.10 = sitofp i64 %var9 to double
store double %conv.10, ptr %ptr.y.11
%ptr.z.15 = alloca double
%val14 = fadd double 0.0, 3.14
store double %val14, ptr %ptr.z.15
%ptr.w.20 = alloca i64
%var18 = load double, ptr %ptr.z.15
%conv.19 = fptosi double %var18 to i64
store i64 %val19, ptr %ptr.w.20
%val21 = add i64 0, 0
ret i64 %val21
}I/O
Balbismo supports printf and scanf-style I/O with format strings.
String literals are hoisted as global LLVM constants. Calls lower to varargs @printf/@scanf.
🔍 View Generated LLVM IR
@str.0 = private constant [10 x i8] c"Hello %d\0A\00"
declare i32 @printf(i8*, ...)
declare i32 @scanf(i8*, ...)
define i64 @main() {
entry:
%val4 = add i64 0, 42
call i32 (i32*, ...) @printf(i8* @str.0, i64 %val4)
%val6 = add i64 0, 0
ret i64 %val6
}Semantics Highlights
- Lex/Yacc (Flex/Bison) define the grammar and construct an AST.
- Dart semantic/IR layer walks the AST and emits LLVM IR.
- Symbol table supports lexical scopes and function registry.
- Arrays support runtime sizes and are stack-allocated; element access is bounds-agnostic (no runtime checks).
- All integers are 64-bit; all floats are double-precision.
- Booleans use
int0/1; logical ops returnint.
Grammar (EBNF)
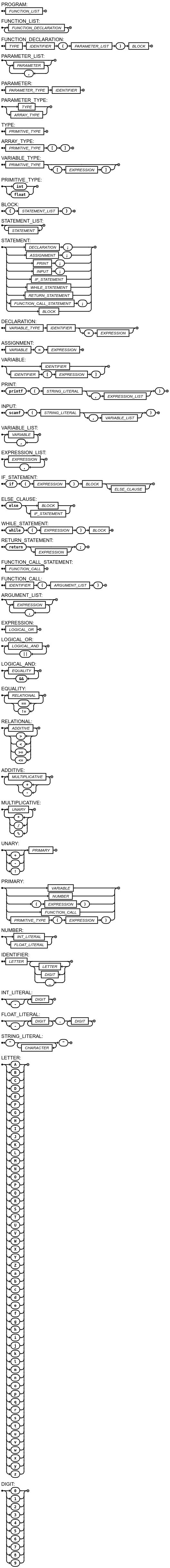
For the complete grammar, see the EBNF and syntax diagram on the main page. Key excerpts:
PROGRAM = FUNCTION_LIST ;
FUNCTION_DECLARATION = TYPE, IDENTIFIER, '(', PARAMETER_LIST, ')', BLOCK ;
PARAMETER_TYPE = TYPE | ARRAY_TYPE ;
VARIABLE_TYPE = PRIMITIVE_TYPE, [ '[', EXPRESSION, ']' ] ;
PRIMITIVE_TYPE = 'int' | 'float' ;
STATEMENT = DECLARATION | ASSIGNMENT | PRINT | INPUT | IF_STATEMENT | WHILE_STATEMENT | RETURN_STATEMENT | FUNCTION_CALL_STATEMENT | BLOCK ;Syntax Diagram
Visual syntax diagram for the full language grammar.